- Deep Research Global
- Posts
- Walmart SWOT Analysis (2026): A Comprehensive Strategic Review
Walmart SWOT Analysis (2026): A Comprehensive Strategic Review
Walmart stands as the world's largest retailer, continuing to dominate the retail industry with impressive financial performance and strategic innovation.
As we move through 2025 and approach 2026, understanding Walmart's strategic position through a comprehensive SWOT analysis reveals critical insights into how this retail giant maintains its market leadership while adapting to rapidly changing consumer preferences and technological disruptions.
Table of Contents
Understanding Walmart's Current Market Position
Walmart's position as the global retail leader remains unchallenged.
The company generated total revenues of $648.1 billion in fiscal year 2024, with fiscal 2025 showing continued growth to $680.985 billion, representing a 5.07% increase. The company maintains a 6.04% market share in the U.S. retail market and operates over 10,482 locations in 24 countries.
What makes Walmart's performance particularly remarkable is its success across multiple channels.
In Q2 FY26, the company achieved 26% e-commerce growth in Walmart U.S., while maintaining 4.8% consolidated revenue growth on a constant currency basis.
This demonstrates the company's ability to balance traditional retail operations with digital transformation.
Strengths: The Foundation of Walmart's Dominance
Unparalleled Scale and Market Presence
Walmart's most significant strength lies in its massive operational scale. The company operates thousands of stores globally, creating an extensive physical footprint that competitors struggle to match.
According to statistics, 90% of the U.S. population lives within 10 miles of a Walmart store, providing unmatched accessibility and convenience for customers.
This scale translates into substantial competitive advantages. The company's purchasing power enables it to negotiate favorable terms with suppliers, maintaining its "Everyday Low Prices" (EDLP) strategy that attracts cost-conscious consumers.
Walmart's fiscal 2025 revenue of $680.985 billion demonstrates the company's ability to leverage this scale effectively.
Advanced Supply Chain and Distribution Network
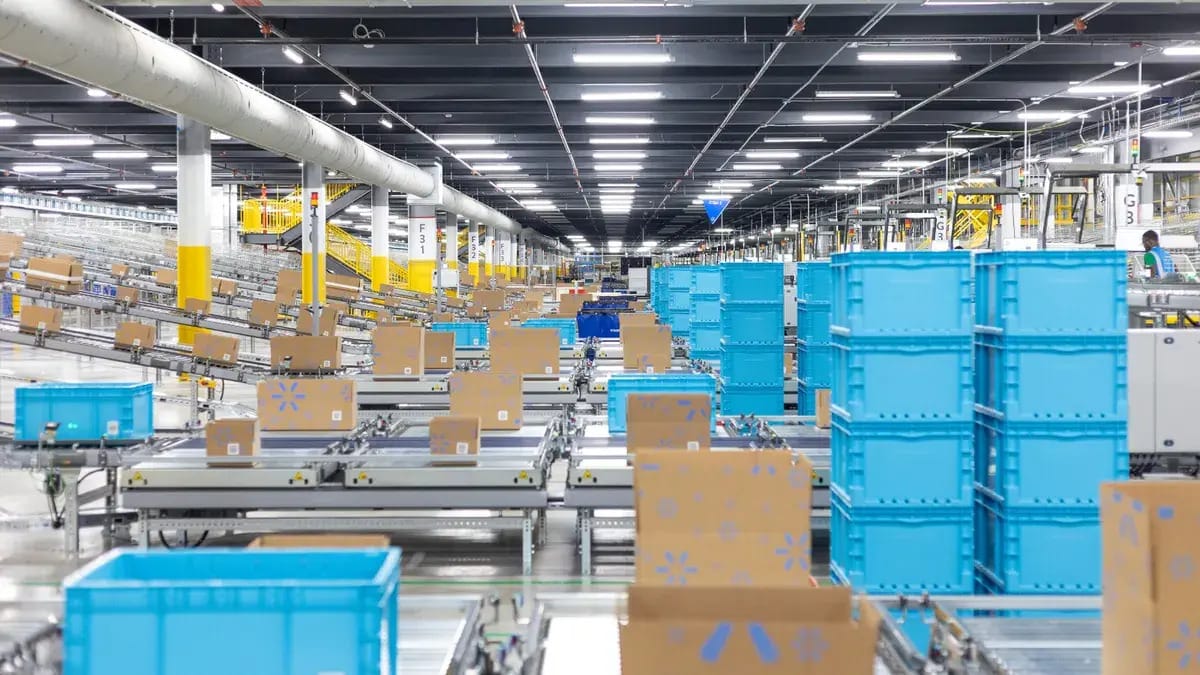

Walmart's supply chain represents a masterclass in logistics excellence.
The company operates over 150 distribution centers worldwide, supported by hundreds of transportation assets. The retailer has invested heavily in automation technology, planning to add five new automated distribution centers to its grocery supply chain.
Walmart's U.S. supply chain playbook is going global, with real-time AI and automation being deployed across international markets. This global supply chain transformation enables faster delivery times, reduced costs, and improved inventory management.
The company's emphasis on efficiency has resulted in significant cost savings through continued automation efforts.
Digital Transformation and E-commerce Success
Walmart has successfully transformed itself into an omnichannel powerhouse.
The company's e-commerce performance has been exceptional, with U.S. e-commerce sales increasing 26% year over year and international e-commerce sales growing 22%.
The retailer has reduced e-commerce losses by 80% in 2024 alone, demonstrating improved operational efficiency in digital channels.
The company's digital ecosystem includes robust mobile applications, convenient pickup and delivery services, and an expanding marketplace platform.
Walmart Marketplace achieved more than 30% sales growth in each of the past four quarters, significantly driving the retailer's sustained e-commerce momentum.
Artificial Intelligence and Technology Innovation
Walmart has embraced artificial intelligence as a core component of its future strategy. The company announced a partnership with OpenAI to create AI-first shopping experiences, allowing customers to shop with ChatGPT.
This integration represents a significant advancement in personalized retail experiences.
The retailer unveiled its strategy to accelerate Adaptive Retail through scaling artificial intelligence, generative AI, augmented reality, and immersive commerce experiences.
Additionally, Walmart deployed AI-powered tools across its U.S. associate base, including real-time translation and task management capabilities for 1.5 million associates.
Diversified Revenue Streams
Walmart has successfully diversified its business model beyond traditional retail.
The company's global advertising business grew 46% in Q2 FY26, with Walmart Connect in the U.S. growing 31%. This high-margin business contributes significantly to profitability.
Membership programs represent another growing revenue stream. Global membership fee income increased 15.3%, driven by steady growth in Sam's Club member counts and renewal rates, plus increased penetration of Plus members.
Walmart+ membership income grew double digits, demonstrating strong consumer adoption of the company's subscription service.
Strong Private Label Portfolio
Walmart launched Bettergoods in April 2024, representing its largest private brand food launch in 20 years. The brand includes approximately 300 items spanning frozen food, dairy, snacks, beverages, pasta, soups, coffee, and chocolate, with most items priced under $5.
Bettergoods has become one of the fastest-growing private label brands in retail. Consumer response has been positive, with 78% planning to repurchase the brand and 46% finding it to be a better value compared to other brands. This success strengthens Walmart's ability to differentiate its offerings and improve profit margins.
Weaknesses: Areas Requiring Strategic Attention
Thin Profit Margins
Despite impressive revenue figures, Walmart operates on notably thin profit margins typical of the discount retail sector. The EDLP strategy, while attracting customers, puts constant pressure on profitability. Any increase in operational costs, supplier prices, or competitive pressure can significantly impact the bottom line.
The company faces ongoing challenges balancing price competitiveness with margin expansion. While higher-margin businesses like advertising are growing, the core retail operations continue to face margin constraints that limit financial flexibility.
Labor Relations and Workforce Challenges
Walmart has historically faced criticism regarding wages, benefits, and working conditions. While the company has made improvements, including implementing AI-powered tools for 1.5 million associates, labor relations remain an ongoing challenge.
High employee turnover in retail positions creates training costs and can affect customer service quality. Maintaining a satisfied and productive workforce while controlling labor costs represents a persistent challenge for the organization.
Limited International Success in Certain Markets
While Walmart has achieved success in markets like Mexico, Canada, and China, the company has experienced failures in markets like Germany and South Korea, where it eventually exited. These experiences highlight the difficulty of adapting the Walmart model to diverse cultural contexts and established local competitors.
International operations, while growing, still face challenges related to cultural adaptation, local competition, and regulatory compliance across different countries.
E-commerce Profitability Challenges
Although Walmart has reduced e-commerce losses by 80%, achieving full profitability in online operations remains challenging. The costs associated with fulfillment, delivery, and returns continue to impact margins in the digital channel.
The company must balance investment in e-commerce infrastructure with profitability expectations, particularly as competition from Amazon and other digital-first retailers intensifies.
Brand Perception Limitations
Walmart's strong association with discount pricing can sometimes limit its ability to attract premium-conscious consumers. Despite efforts like Bettergoods to elevate its product offerings, some customer segments still perceive Walmart primarily as a low-cost option rather than a quality or experience destination.
This perception can restrict the company's ability to expand into higher-margin product categories or attract more affluent demographic segments.
Opportunities: Paths for Future Growth
International Market Expansion
Walmart has significant opportunities for growth in international markets, particularly in high-growth economies. The company plans to reach $200 billion in gross merchandise volume in foreign markets within five years, double its current rate. The company focuses on key markets like China, India, and Mexico.
International e-commerce represents a particularly promising avenue, with 22% growth in Walmart International e-commerce, led by store-fulfilled pickup and delivery services plus third-party marketplace expansion.
Healthcare and Wellness Services
The healthcare sector offers substantial growth potential. Walmart has been expanding its healthcare services, including in-store clinics, pharmacy services, and telehealth options. The aging U.S. population and increasing healthcare costs create opportunities for affordable, accessible healthcare solutions through Walmart's extensive store network.
Integrating healthcare with retail shopping provides convenience for customers while creating higher-margin revenue streams and increasing store traffic.
Sustainability and Environmental Leadership
Walmart has ambitious sustainability goals through Project Gigaton, aimed at reducing one billion metric tons of greenhouse gas emissions from its global supply chain by 2030. The company achieved this goal six years early, demonstrating significant leadership in corporate sustainability.
Consumer preference for sustainable products continues growing. Walmart's commitment to making sustainable choices easy, accessible and affordable for customers can strengthen brand loyalty and attract environmentally conscious consumers. The company's sustainability initiatives include renewable energy adoption, waste reduction, and responsible sourcing practices.
Financial Services Expansion
Walmart has opportunities to expand its financial services offerings, including banking, lending, payment solutions, and insurance products. The company's existing customer base and trusted brand provide a foundation for financial service innovations that could serve underbanked populations while generating new revenue streams.
Mobile payment solutions and digital wallets integrated with Walmart's shopping ecosystem can enhance customer convenience while collecting valuable transaction data for personalization and marketing.
Automation and Robotics
Continued investment in automation and robotics can drive operational efficiency. Walmart is expanding automated distribution centers and implementing autonomous forklifts and other robotics solutions. These technologies can reduce labor costs, improve accuracy, and accelerate fulfillment speeds.
In-store automation, including self-checkout systems, inventory management robots, and automated picking systems, can enhance the customer experience while optimizing labor deployment.
The success of Bettergoods demonstrates consumer appetite for elevated products at accessible prices. Walmart can continue expanding into premium and specialty categories, including organic foods, artisanal products, and trend-forward items that attract new customer demographics.
This strategy allows Walmart to compete beyond price alone, building brand loyalty based on quality, uniqueness, and value rather than just low cost.
Intense Competition from Amazon and Digital Retailers
Amazon remains Walmart's most formidable competitor. Amazon holds a 37.6% share of U.S. e-commerce, compared to Walmart's 6.4%. This gap highlights the ongoing challenge Walmart faces in digital retail.
Amazon's advantages include superior logistics infrastructure, Prime membership loyalty, and technology capabilities. The competition extends beyond online sales to include cloud computing, entertainment content, and smart home devices, creating an integrated ecosystem that competes for consumer wallet share.
Economic Uncertainty and Consumer Spending
Economic volatility, including inflation, recession risks, unemployment, and interest rate fluctuations, directly impacts consumer spending at discount retailers. During economic downturns, even value-focused consumers reduce spending or trade down to even cheaper alternatives.
Walmart's customer base includes many price-sensitive consumers who are particularly affected by economic challenges, creating vulnerability during economic downturns.
Supply Chain Disruptions
Global supply chain challenges have been highlighted by recent events including pandemics, geopolitical tensions, and natural disasters. Walmart's international sourcing and complex logistics network create vulnerability to disruptions that can affect product availability, increase costs, and damage customer satisfaction.
Climate change may increasingly impact supply chains through extreme weather events, requiring adaptive strategies and resilient infrastructure.
Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
As a global retailer, Walmart faces complex and evolving regulatory environments across multiple jurisdictions. Issues include labor laws, environmental regulations, data privacy requirements, antitrust concerns, and international trade policies.
Compliance costs can be substantial, and regulatory changes can require significant operational adjustments. Violations can result in financial penalties and reputational damage.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy Risks
Walmart's digital transformation increases exposure to cybersecurity threats. The company collects vast amounts of customer data through online transactions, mobile apps, and loyalty programs. Data breaches could result in financial losses, legal liabilities, and erosion of customer trust.
Evolving data privacy regulations require ongoing investment in security infrastructure and compliance systems.
Changing Consumer Preferences
Consumer preferences continue evolving toward experiences over products, sustainability, convenience, and personalization. Walmart must continuously adapt to these shifts or risk losing relevance, particularly among younger consumer segments.
The rise of social commerce, influencer marketing, and direct-to-consumer brands creates new competitive dynamics that challenge traditional retail models.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 and Beyond
Based on this comprehensive SWOT analysis, several strategic priorities emerge for Walmart as it positions itself for sustained success:
Accelerate Digital Transformation: Continue investing in e-commerce infrastructure, AI capabilities, and omnichannel integration. The partnership with OpenAI and deployment of AI-powered tools for associates represent important steps that should be expanded.
Expand High-Margin Businesses: Grow advertising, financial services, and healthcare offerings to diversify revenue and improve profitability. The 46% growth in global advertising business demonstrates the potential of these initiatives.
Strengthen International Presence: Focus on high-growth markets while learning from past international expansion challenges. The goal of $200 billion in international gross merchandise volume represents an ambitious but achievable target.
Enhance Sustainability Leadership: Build on the success of Project Gigaton to further establish Walmart as a sustainability leader, recognizing that environmental considerations increasingly influence consumer choices.
Optimize the Private Label Portfolio: Continue developing and promoting private brands like Bettergoods that offer differentiation beyond price while maintaining attractive margins.
Invest in Supply Chain Resilience: Expand automation while building flexibility to respond to disruptions. The global deployment of supply chain AI and automation positions the company well.
My Final Thoughts
Walmart's SWOT analysis for 2026 and beyond reveals a company leveraging formidable strengths while actively addressing weaknesses and pursuing strategic opportunities.
The retailer's scale, supply chain excellence, and digital transformation position it to compete effectively despite intense competitive pressures and market uncertainties.
The company's fiscal 2025 revenue of $680.985 billion and impressive e-commerce growth of 26% demonstrate continued strength. Success in initiatives like Bettergoods, AI integration, and advertising business growth shows Walmart's ability to innovate and adapt.
Key challenges include maintaining margins, competing with Amazon's digital dominance, and navigating economic and regulatory uncertainties. However, Walmart's focus on value, convenience, and innovation through its omnichannel strategy positions it well for continued market leadership.
As retail continues evolving, Walmart's ability to balance its traditional strengths with forward-looking investments in technology, sustainability, and new business models will determine its success in 2026 and beyond.
The company's comprehensive approach to strategic planning, evident in this SWOT analysis, suggests it is well-prepared to maintain its position as the world's leading retailer.
Reply