- Deep Research Global
- Posts
- Coca-Cola - Company Analysis and Outlook Report (2026)
Coca-Cola - Company Analysis and Outlook Report (2026)
Executive TL;DR
Q3 2025 Performance: Coca-Cola $KO ( ▲ 1.32% ) delivered 6% organic revenue growth with net revenues reaching $12.5 billion, driven by 6% price/mix growth despite flat concentrate sales.
Financial Strength: Operating margin expanded to 32.0%, while comparable EPS grew 6% to $0.82, demonstrating pricing power amid challenging macro conditions.
2026 Outlook: Management projects 5-6% organic revenue growth with slight currency tailwinds, positioning the company for continued value creation.
Valuation Tension: Wall Street analysts set a consensus price target of $79.08, suggesting modest upside from current levels around $70, while DCF analyses show mixed signals.
Also Read:
Table of Contents

Image source: coca-colacompany.com
Business Overview and Key Facts
The Coca-Cola Company stands as the world’s largest nonalcoholic beverage corporation, operating in more than 200 countries. Founded in 1886, the Atlanta-based company has built an unmatched global distribution network through its franchise business model.
The company generates revenue through two primary channels. First, it sells concentrates and syrups to bottling partners worldwide. Second, it sells finished beverages directly to retailers in certain markets.
Revenue Snapshot
For the last twelve months (LTM) ending September 2025, Coca-Cola reported total revenues of $36.1 billion. This represents steady growth despite facing headwinds in several markets.
The geographic revenue breakdown demonstrates global diversification:
Geographic Segment | Q3 2025 Organic Revenue Growth | Volume Performance |
|---|---|---|
Europe, Middle East & Africa | 7% | +4% |
Latin America | 4% | Flat |
North America | 4% | Flat |
Asia Pacific | 7% | -1% |
Core Product Lines
Coca-Cola operates across five major beverage categories. Sparkling soft drinks remain the cornerstone, generating the majority of revenue.
Trademark Coca-Cola grew 1% in Q3 2025. Coca-Cola Zero Sugar surged 14%, reflecting the consumer shift toward healthier options. Diet Coke/Coca-Cola Light expanded 2%, primarily driven by North American demand.
The water, sports, coffee and tea segment grew 3%. Sports drinks advanced 3%, with the dual-brand strategy of Powerade and BODYARMOR gaining traction. The company’s ready-to-drink tea portfolio maintained global category leadership.
Value-added dairy represents a growing opportunity. The fairlife portfolio continues expanding in the United States. In Mexico, Santa Clara captured the value share leadership position with 13% volume growth during Q3 2025.
Latest Strategic Developments and News
Product Innovation Pipeline
Coca-Cola has accelerated its innovation cadence. Starting January 1, 2026, the company will introduce 7.5-ounce mini cans as single-serve options in convenience stores for the first time.
The Orange Cream flavor innovation launched in early 2025. Coca-Cola Orange Cream and Coca-Cola Zero Sugar Orange Cream remain available through early 2026. This represents a deliberate strategy to refresh flavor offerings continuously.
Minute Maid Zero Sugar has expanded into select Asia Pacific markets. The brand shows strong consumer interest and solid volume performance, building on North American success.
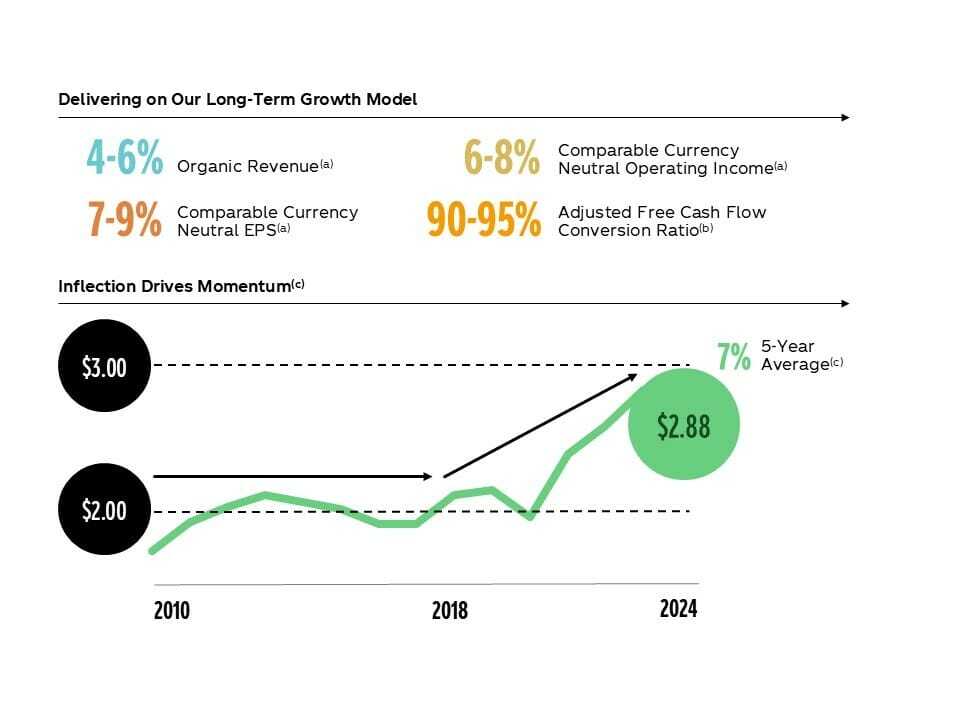
Image source: investors.coca-colacompany.com
Bottling System Transformation
The company’s franchise model evolution continues. In October 2025, Coca-Cola HBC AG announced a definitive agreement to acquire a controlling interest in Coca-Cola Beverages Africa (CCBA).
This refranchising step consolidates operations under a proven bottler. CCHBC brings strong operational expertise in African markets. The transaction strengthens the overall system’s capability to drive growth.
In India, the company sold a 40% ownership stake in Hindustan Coca-Cola Holdings to Jubilant Bhartia Group in July 2025. This represents another milestone in optimizing the bottling network.
Functional Beverage Expansion
The company has intensified its focus on functional beverages. The fairlife portfolio continues expanding, meeting consumer demand for protein-enriched dairy products.
BODYARMOR made its European debut in Spain during 2025. The brand’s international expansion leverages insights from its U.S. success against Gatorade. The Brussels innovation team adapted formulations for European consumer preferences.
China Market Optimism
Despite broader Asia Pacific challenges, management remains optimistic about China. The company is developing granular market strategies and customer-specific execution plans.
China contributed to Q1 2025 global unit case volume growth of 2%. The system continues investing in supply chain capabilities to support long-term expansion.
Competitive Analysis and Moat Assessment
Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Competitive Rivalry: Intense
The nonalcoholic beverage industry faces fierce competition. PepsiCo remains the primary rival across multiple categories. According to Q2 2025 market data, PepsiCo commands 53.31% market share in nonalcoholic beverages compared to Coca-Cola’s 27.35% based on total revenues.
However, this comparison includes PepsiCo’s substantial snack food business. In carbonated soft drinks specifically, Coca-Cola maintains global leadership. The company holds approximately 40% of the global CSD market.
Keurig Dr Pepper poses competitive threats in North America, particularly with Dr Pepper and 7UP. Regional players like Vita Coco in coconut water and Monster in energy drinks capture niche segments.
Threat of New Entrants: Low to Moderate
Significant barriers protect established beverage companies. Capital requirements for nationwide distribution networks exceed billions of dollars. Brand recognition takes decades to build.
However, smaller premium and functional beverage brands can enter through targeted distribution. Direct-to-consumer channels lower entry barriers for niche players. These brands often target health-conscious consumers willing to pay premium prices.
Bargaining Power of Suppliers: Low
Coca-Cola sources commodities from global markets. Key inputs include sugar, HFCS, PET resin, aluminum, and water. The company’s massive scale provides procurement advantages.
Multiple suppliers exist for most raw materials. Long-term contracts lock in favorable pricing. Currency hedging programs mitigate foreign exchange volatility.
Aluminum tariffs represent a potential exception. Management mentioned possible shifts toward plastic bottles if aluminum costs spike. This flexibility limits supplier power.
Bargaining Power of Buyers: Moderate
Retail consolidation has increased buyer power. Large retailers like Walmart, Kroger, and Amazon command significant negotiating leverage. They can demand promotional support and favorable pricing.
However, Coca-Cola’s brand strength provides countervailing power. Retailers need popular brands to drive foot traffic. The company gained value share in total NARTD beverages during Q3 2025, demonstrating ongoing consumer demand.
Threat of Substitutes: High
Health trends drive substitution threats. Consumers increasingly choose water, unsweetened tea, and functional beverages over traditional sodas. Premium coffee chains compete for consumption occasions.
The CSD market faces headwinds in developed markets. Coca-Cola’s flagship brand posted -3.4% dollar sales decline at U.S. retail in the first nine months of 2025.
Coca-Cola addresses this through portfolio diversification. Zero sugar variants, sports drinks, and value-added dairy reduce reliance on core CSD products.
Competitive Factor | Assessment | Impact on Moat |
|---|---|---|
Brand Strength | Very Strong | Positive |
Distribution Network | Global, Unmatched | Positive |
Scale Economies | Significant | Positive |
Switching Costs | Low for Consumers | Negative |
Innovation Speed | Improving | Neutral |
Coca-Cola gained value share in Q3 2025 across multiple regions. Latin America showed particular strength with share gains in Brazil and Argentina. North America captured gains in juice, dairy, and sports beverages.
Asia Pacific gained share in the Philippines and Japan. However, China remains challenging. The company faces intense local competition in lower-tier cities.
Europe, Middle East and Africa showed mixed results. Gains in Egypt and Kazakhstan offset declines in South Africa and Pakistan.
Competitive Moat Strength
Coca-Cola’s competitive moat remains wide but faces erosion pressure. Brand value represents the strongest moat element. Interbrand consistently ranks Coca-Cola among the world’s most valuable brands.
The global distribution network provides competitive advantage. Reaching remote villages in India or stores in Sub-Saharan Africa requires decades of relationship building. New entrants cannot replicate this infrastructure quickly.
Scale economies in marketing, procurement, and R&D create cost advantages. Coca-Cola spreads fixed costs across enormous volume. This enables higher profitability per unit than smaller competitors.
However, consumer switching costs remain low. Taste preferences shift relatively easily. Health trends accelerate substitution. The company must continuously innovate to maintain relevance.
Network effects do not significantly benefit beverage companies. A customer’s choice of soft drink doesn’t increase value for other consumers. This differs from technology platforms.
Image source: coca-colahellenic.com
Financial Deep Dive
Historical Revenue Trends
Coca-Cola demonstrated resilience through recent quarters. Q3 2025 net revenues grew 5% to $12.5 billion. Organic revenues expanded 6%, adjusting for currency and structural changes.
Year-to-date through September 2025, revenues reached $36.1 billion. This represented 2% growth on a reported basis despite a 3% currency headwind.
The nine-month period showed:
Revenue Growth Components (9M 2025):
- Price/Mix: +6%
- Concentrate Sales: Flat
- Currency Impact: -3%
- Structural Changes: -1%
- Reported Growth: +2%
Price/mix contributed all organic growth. Volume remained essentially flat. This pattern reflects challenging consumer environments across developed markets.
Profitability Margins
Operating margin expanded significantly. Q3 2025 operating margin reached 32.0% versus 21.2% in the prior year. Items impacting comparability boosted reported figures.
Comparable operating margin (non-GAAP) was 31.9% versus 30.7% a year earlier. This 120 basis point expansion came from organic revenue growth and effective cost management. Higher marketing investments partially offset gains.
Gross margin has remained strong. Recent data shows gross margin at 61.63%, reflecting favorable pricing and product mix.
Margin Metric | Q3 2025 | Q3 2024 | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
Gross Margin | ~62% | ~62% | Stable |
Operating Margin | 32.0% | 21.2% | +1,080 bps |
Comparable Operating Margin | 31.9% | 30.7% | +120 bps |
Net Margin | ~30% | ~24% | +600 bps |
Return Metrics
Return on equity (ROE) stands exceptionally strong. Current ROE measures 47.01% as of January 2026. This represents a 302.64% increase compared to the four-quarter average of 11.67%.
The dramatic ROE improvement reflects higher net income combined with share repurchases reducing equity. ROE fluctuations partly result from fairlife contingent payments and other extraordinary items.
Return on assets (ROA) reached 14.05% in Q3 2025. This demonstrates efficient asset utilization relative to peers.
The company’s asset-light franchise model drives superior returns. Bottling partners own most manufacturing and distribution assets. Coca-Cola focuses on brand building and concentrate production.
Free Cash Flow Analysis
Cash generation remains strong despite temporary distortions. Year-to-date through September 2025, operating cash flow was $3.7 billion. Free cash flow reached $2.4 billion.
However, these figures include the $6.1 billion fairlife contingent consideration payment made in Q1 2025. This one-time payment related to the 2020 acquisition.
Excluding the fairlife payment, free cash flow (non-GAAP) totaled $8.5 billion year-to-date. This demonstrates the underlying cash generation power.
Management projects full-year 2025 free cash flow excluding the fairlife payment of at least $9.8 billion. This consists of:
2025 Free Cash Flow Guidance:
Operating Cash Flow: ~$12.0 billion
Less: Capital Expenditures: ~$2.2 billion
Free Cash Flow: ~$9.8 billion
Capital expenditures remain modest at approximately 18% of operating cash flow. The franchise model limits required investments.
Balance Sheet Strength
Total debt stands at $48.16 billion as of the most recent quarter. Total cash reaches $15.78 billion. Net debt therefore approximates $32.4 billion.
The debt-to-equity ratio measures 144.77%, or approximately 1.45x. This reflects moderate leverage. Management targets net debt leverage of 2.0 to 2.5 times comparable EBITDA.
Current leverage ratios sit comfortably within target ranges. The company maintains investment-grade credit ratings. S&P rates Coca-Cola HBC at BBB+, reflecting solid financial health.
Interest coverage remains robust. EBIT covers interest expense by approximately 34.1 times. This massive coverage ratio eliminates near-term refinancing concerns.
Balance Sheet Metric | Value |
|---|---|
Total Cash | $15.78 billion |
Total Debt | $48.16 billion |
Net Debt | ~$32.4 billion |
Debt-to-Equity | 1.45x |
Current Ratio | 1.21x |
Valuation Analysis
Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Modeling
DCF analyses show divergent conclusions depending on assumptions. Conservative models suggest potential overvaluation. More optimistic scenarios indicate undervaluation.
A recent DCF analysis estimated fair value at $67.50, implying slight overvaluation at current prices around $70. This model likely uses conservative growth assumptions.
However, another DCF calculation estimated intrinsic value at $78.25 per share. This suggests modest undervaluation. The difference hinges on terminal growth rates and discount rates.
Simply Wall Street’s DCF model indicates Coca-Cola is undervalued by 23.2%. Their analysis likely incorporates international expansion opportunities.
Key DCF variables include:
Critical DCF Assumptions:
- Free Cash Flow Growth Rate (Years 1-5): 4-7%
- Terminal Growth Rate: 2.5-3.5%
- Weighted Average Cost of Capital: 6.5-8.0%
- Terminal FCF Margin: 22-26%
Higher terminal growth rates favor bulls. Bears point to mature market saturation limiting long-term growth. The truth likely falls between extremes.
Comparable Company Analysis
Relative valuation metrics show Coca-Cola trading at premium multiples. The current P/E ratio stands at approximately 22.96 on a TTM basis.
This exceeds the S&P 500 average P/E of roughly 20-21. It also surpasses PepsiCo’s P/E ratio. The premium reflects Coca-Cola’s brand strength and global reach.
Price-to-sales ratio measures approximately 5.5x. This compares favorably to premium consumer brands but exceeds broader beverage industry averages.
EV/EBITDA multiples approximate 18-20x. This valuation multiple has remained relatively stable over the past year despite market volatility.
Valuation Metric | Coca-Cola (KO) | PepsiCo (PEP) | Industry Average |
|---|---|---|---|
P/E Ratio (TTM) | 22.96x | ~21x | ~19x |
P/S Ratio | ~5.5x | ~2.8x | ~2.2x |
EV/EBITDA | ~19x | ~17x | ~14x |
Dividend Yield | 2.89% | 2.9% | 2.5% |
Sensitivity Analysis
Valuation outcomes vary significantly with assumption changes. Terminal growth rate sensitivity proves particularly important.
DCF Sensitivity to Terminal Growth Rate:
Terminal Growth 2.0%: Fair Value ~$65
Terminal Growth 2.5%: Fair Value ~$72
Terminal Growth 3.0%: Fair Value ~$80
Terminal Growth 3.5%: Fair Value ~$90
WACC sensitivity also matters substantially:
DCF Sensitivity to WACC:
WACC 6.5%: Fair Value ~$85
WACC 7.0%: Fair Value ~$76
WACC 7.5%: Fair Value ~$69
WACC 8.0%: Fair Value ~$63
These ranges illustrate valuation uncertainty. Small assumption changes drive large value swings. Investors should stress-test their own models across scenarios.
Dividend Discount Model
Coca-Cola’s 63-year dividend growth streak makes dividend discount models relevant. The current quarterly dividend is $0.51 per share, or $2.04 annualized.
Dividend yield stands at 2.89%. The payout ratio measures approximately 65-67%. This leaves room for continued dividend growth while maintaining financial flexibility.
Historical dividend growth has averaged 4.0% over the past five years and 4.3% over the past decade. Management typically increases dividends annually in February or March.
Applying a Gordon Growth Model with conservative assumptions:
Gordon Growth Model:
Current Dividend: $2.04
Expected Growth Rate: 4%
Required Return: 8%
Fair Value = $2.04 × (1.04) / (0.08 - 0.04) = $53
More Optimistic Scenario:
Expected Growth Rate: 5%
Required Return: 7.5%
Fair Value = $2.04 × (1.05) / (0.075 - 0.05) = $86
The wide range again demonstrates assumption sensitivity. Dividend growth investors focusing on income stability may find current yields attractive despite valuation concerns.
Catalysts and Timeline
Near-Term Catalysts (2026)
Q4 2025 Earnings Release (February 2026)
Fourth-quarter results will reveal full-year 2025 performance. Management projects comparable EPS growth of approximately 3% for the year. Currency provides a slight tailwind in Q4 versus prior-year comparisons.
Holiday season performance matters significantly. Carbonated soft drinks see elevated consumption during year-end celebrations. Promotional effectiveness will determine market share outcomes.
2026 Guidance Announcement (February 2026)
Management will provide full-year 2026 guidance alongside Q4 results. Preliminary commentary suggests 5-6% organic revenue growth remains achievable.
Currency should provide modest tailwinds based on current rates. This reverses the headwinds faced throughout 2025. Each percentage point of currency benefit drops more directly to earnings.
Innovation Launches (Q1-Q2 2026)
New product introductions should support growth acceleration. The 7.5-ounce mini can rollout begins January 1, 2026. This targets convenience store growth.
Coca-Cola Cherry Float debuts in April 2026. Diet Cherry Coke returns permanently in early 2026. These flavor innovations target younger consumers seeking variety.
Medium-Term Catalysts (2026-2027)
Emerging Market Expansion
India represents a major growth opportunity. The Jubilant Bhartia partnership should accelerate distribution expansion. India’s beverage market remains underpenetrated relative to developed markets.
Africa presents similar potential following the CCHBC/CCBA transaction. Consolidating bottling operations under proven management should unlock efficiency gains. Rising middle-class populations drive long-term volume growth.
China recovery remains uncertain but impactful. Any reacceleration in Chinese consumer spending would benefit Coca-Cola significantly. The company maintains market leadership positions to capture upside.
Zero Sugar Momentum
Coca-Cola Zero Sugar growth of 14% in Q3 2025 demonstrates secular trends. Health-conscious consumers continue shifting from full-sugar variants. The company has improved Zero Sugar taste profiles through reformulation.
If Zero Sugar maintains double-digit growth, it could offset traditional Coke declines. The higher-margin product also benefits profitability. Marketing investments behind Zero Sugar should continue.
BODYARMOR International
The European launch in Spain represents early innings of international expansion. Success in Europe could justify broader rollouts across developed markets. BODYARMOR competes in the fast-growing sports drink category.
Displacing Gatorade internationally would require years of investment. However, even capturing 10-15% market share in large markets adds meaningful revenue.
Long-Term Catalysts (2027+)
Sustainability Initiatives
Coca-Cola targets net zero emissions by 2040. ESG-conscious investors may reward progress with higher valuation multiples.
Packaging innovations reduce plastic usage. The company has committed to making packaging 100% recyclable. Water stewardship programs address environmental criticism.
However, plastic pollution remains a significant reputational risk. Increased regulation could raise packaging costs. Success mitigating environmental impacts creates long-term value.
Digital and AI Integration
Coca-Cola has invested in artificial intelligence for marketing and operations. AI enables personalized advertising at scale. It also optimizes supply chain and inventory management.
Digital vending machines collect real-time consumption data. This informs product placement and pricing decisions. Continued digital transformation should drive margin expansion over time.
Functional Beverage Platform
Protein shakes, enhanced waters, and energy drinks represent faster-growing categories. Coca-Cola has assembled capabilities through fairlife, BODYARMOR, and other acquisitions.
Building a leadership position in functional beverages diversifies away from declining CSD markets. This requires sustained innovation investment but offers superior long-term growth rates.
Catalyst Category | Timeframe | Probability | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
2026 Guidance Beat | Near-term | Medium | +5-8% |
Zero Sugar Acceleration | Near-term | High | +3-5% |
China Reacceleration | Medium-term | Low-Medium | +8-12% |
BODYARMOR International Success | Long-term | Medium | +5-10% |
Functional Platform Leadership | Long-term | Medium | +10-15% |
Key Risks and Scenarios
Health and Wellness Trends (Probability: High)
Consumer preferences continue shifting toward healthier options. This represents the most significant long-term risk. Traditional full-calorie sodas face declining demand in developed markets.
The Coca-Cola flagship posted -3.4% dollar sales decline at U.S. retail in the first nine months of 2025. Volume fell -8.0%. This trend could accelerate.
Zero sugar and diet variants partially offset declines. However, artificial sweetener concerns limit adoption among some consumers. Natural sweetener alternatives remain expensive.
Base Case Scenario: CSD volumes decline 1-2% annually in developed markets. Zero sugar growth of 10-15% partially offsets declines. Net impact reduces total sparkling volumes by 0-1% annually.
Bear Case Scenario: Health trends accelerate. CSD volumes fall 3-4% annually in developed markets. Regulatory sugar taxes expand globally. Coca-Cola struggles to adapt portfolio quickly enough. Stock underperforms by 10-20% over five years.
Bull Case Scenario: Zero sugar becomes the dominant CSD choice. Total CSD volumes stabilize. Coca-Cola captures share from smaller brands. Stock outperforms by 10-15% over five years.
Regulatory and Tax Risks (Probability: Medium-High)
Sugar taxes have spread globally. More than 50 countries have implemented some form of sugar-sweetened beverage tax. These directly impact demand through higher prices.
Mexico’s sugar tax serves as a warning. Consumption declined following implementation. However, Coca-Cola adapted through portfolio shifts toward lower-sugar products.
Additional regulations could target packaging, marketing to children, or environmental impacts. Compliance costs would increase. Revenue growth could slow if advertising restrictions tighten.
Impact Assessment: Medium negative. Annual EBITDA impact of 2-4% possible if regulations expand aggressively. Lower probability of severe restrictions due to industry lobbying power.
Currency and Emerging Market Volatility (Probability: High)
Coca-Cola generates approximately 76% of revenue outside the United States. Currency fluctuations significantly impact reported results.
The company faced 5-6% currency headwinds to EPS in 2025. Dollar strength reduces the translated value of foreign earnings. Hedging programs provide partial protection but cannot eliminate exposure entirely.
Emerging markets offer growth potential but carry political and economic risks. Argentina, Turkey, and Nigeria have experienced severe currency devaluations. Venezuela operations became nearly worthless.
Impact Assessment: Medium negative. Currency volatility increases earnings uncertainty. However, geographic diversification provides natural hedges. Long-term growth prospects in emerging markets justify exposure.
Competitive Pressures (Probability: Medium)
PepsiCo remains formidable with superior snack food synergies. Energy drink brands like Monster and Red Bull command premium prices and margins. Premium water brands capture high-end consumers.
Private label beverages gain share during economic downturns. Retailers promote house brands with better margins. Coca-Cola must maintain innovation and marketing investment to defend positions.
Digital-native brands bypass traditional retail. Direct-to-consumer models enable premium pricing. Smaller brands can test products and build loyalty before seeking broader distribution.
Impact Assessment: Medium negative. Market share erosion of 0.5-1.0% annually possible across categories. However, Coca-Cola’s scale advantages and brand strength provide defensive moats.
Commodity Cost Inflation (Probability: Medium)
Aluminum, PET resin, sugar, and HFCS costs fluctuate based on commodity markets. Energy costs impact manufacturing and transportation. Labor costs continue rising in most markets.
Aluminum tariffs represent a specific concern. Management has discussed potential shifts toward plastic bottles if aluminum costs spike. However, plastic carries environmental criticism.
The company’s procurement scale provides advantages. Long-term contracts lock in prices. However, sustained commodity inflation squeezes margins absent offsetting price increases.
Impact Assessment: Low-medium negative. Gross margins could compress 50-100 basis points under sustained inflation. However, pricing power allows partial offset. Net impact manageable over 2-3 years.
Climate and Water Risks (Probability: Medium)
Water scarcity affects both production and reputation. Coca-Cola requires substantial freshwater for manufacturing. Community opposition has halted plant expansions in water-stressed regions.
Climate change may disrupt agricultural supply chains. Extreme weather damages sugar cane and citrus crops. Transportation disruptions increase during severe weather events.
The company has made water replenishment commitments. However, enforcement and verification remain challenging. Failure to meet sustainability goals invites criticism.
Impact Assessment: Low-medium negative over 5-10 years. Climate risks materialize gradually. Early action on sustainability mitigates worst outcomes. Reputation damage represents greater near-term risk than physical disruption.
Risk Factor | Probability | Time Horizon | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
Health Trends | High | Ongoing | -10% to -20% EPS over 5 years |
Regulatory/Tax | Medium-High | 2-5 years | -2% to -4% annual EBITDA |
Currency Volatility | High | Ongoing | -3% to +3% annual EPS |
Competition | Medium | Ongoing | -0.5% to -1% market share annually |
Commodity Inflation | Medium | 1-3 years | -50 to -100 bps gross margin |
Climate/Water | Medium | 5-10 years | -1% to -3% annual EBITDA |
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Unmatched Global Brand Portfolio
Coca-Cola owns 21 billion-dollar brands including Coke, Sprite, Fanta, Dasani, and Powerade. Brand recognition spans virtually every country. This intangible asset provides pricing power and customer loyalty.
Trademark Coca-Cola alone generates tens of billions in annual revenue. The brand transcends product categories, appearing on apparel, collectibles, and entertainment.
World-Class Distribution Network
The company reaches more than 30 million retail outlets globally. This includes remote villages in Africa and Asia. Building comparable distribution would require decades and billions of dollars.
The franchise model leverages local bottlers’ expertise and capital. Coca-Cola focuses resources on marketing and innovation while partners handle manufacturing and logistics.
Financial Strength and Cash Generation
ROE exceeds 40%, demonstrating efficient capital allocation. Operating margins approaching 32% reflect pricing power and scale economies. Free cash flow generation funds dividends, buybacks, and growth investments.
The balance sheet supports acquisitions and opportunistic investments. Investment-grade credit ratings ensure low-cost capital access. Financial flexibility enables strategic agility.
Innovation and R&D Capabilities
Coca-Cola’s global R&D network tests thousands of formulations annually. The company can rapidly scale successful products across markets. Digital tools and AI accelerate product development cycles.
Consumer insights drawn from billions of transactions inform innovation. The company identifies emerging trends before competitors. This enables first-mover advantages in new categories.
Weaknesses
Dependence on Declining CSD Category
Carbonated soft drinks still generate the majority of revenue. CSD volumes decline steadily in developed markets. Diversification into other categories remains incomplete.
The flagship Coca-Cola brand faces particular challenges. Full-calorie variants suffer the steepest declines. Reformulation efforts have not reversed trends.
Emerging Market Exposure
High international revenue mix creates currency volatility. Devaluations in Argentina, Turkey, and other markets reduce translated earnings. Political instability threatens operations and assets.
Some emerging markets show slower-than-expected development. Middle-class expansion has disappointed in certain African countries. Infrastructure limitations constrain distribution expansion.
Limited Direct Consumer Relationships
The franchise model intermediates customer relationships. Bottlers own retail interactions in most markets. This limits Coca-Cola’s direct consumer data and engagement.
Direct-to-consumer brands build deeper customer relationships through subscriptions and digital platforms. Coca-Cola must work through partners, reducing agility.
Sustainability Criticism
Coca-Cola faces ongoing criticism regarding plastic pollution. The company ranks among the world’s largest plastic producers. Beach cleanup data consistently finds Coca-Cola packaging.
Water usage controversies have arisen in India, Mexico, and other water-stressed regions. Communities blame the company for aquifer depletion. Plant expansions face local opposition.
Opportunities
Zero Sugar and Low-Calorie Growth
Zero sugar variants show strong momentum across markets. Improved formulations address prior taste complaints. The category could approach 30-40% of CSD mix within five years.
Low-calorie innovation extends beyond traditional CSDs. Zero sugar sports drinks, teas, and juices capture health-conscious consumers. Margins often exceed full-sugar equivalents.
Functional Beverage Expansion
Protein drinks, enhanced waters, and energy beverages grow faster than traditional categories. Coca-Cola has acquired platforms (fairlife, BODYARMOR) to compete. Additional acquisitions could accelerate growth.
Combining existing distribution with functional beverage innovation creates competitive advantages. The company can bring products to market faster than startups while offering brand credibility.
Premiumization
Consumers trade up to premium products in craft sodas, specialty coffee, and enhanced waters. Premium products command 20-50% higher prices. Margins significantly exceed core products.
Coca-Cola has launched premium extensions like Coca-Cola Signature Mixers and Topo Chico hard seltzer. Further premiumization across the portfolio could drive revenue per case higher.
Digital and E-Commerce
E-commerce beverage sales grow rapidly. Amazon, Instacart, and quick-commerce platforms change purchase behaviors. Coca-Cola must optimize for digital discovery and conversion.
Connected vending machines and fountain equipment collect real-time data. This enables dynamic pricing and personalized recommendations. Digital infrastructure investments should improve capital efficiency over time.
Emerging Middle Class Growth
Long-term demographic trends favor beverage consumption growth. Rising incomes in India, Southeast Asia, and Africa increase affordability. Urbanization changes consumption occasions toward on-the-go beverages.
Despite near-term challenges, multi-decade growth potential remains intact. Patience through economic cycles should reward investors. Market leadership positions Coca-Cola to capture disproportionate growth.
Threats
Intensifying Health Consciousness
Generational shifts accelerate movement away from sugary beverages. Gen Z consumes significantly fewer CSDs than prior generations. Social media amplifies health messaging.
Functional beverages and plain water gain share. Plant-based alternatives attract experimenters. Coca-Cola risks irrelevance among younger consumers without successful portfolio transformation.
Retail Consolidation
Walmart, Amazon, Costco, and other mega-retailers command growing market share. Their bargaining power increases with scale. Promotional spending rises to maintain shelf space and placement.
Private label quality improvements erode brand loyalty. Retailers allocate premium shelf space to house brands. Coca-Cola must demonstrate superior velocity to justify positioning.
Disruptive Competition
Energy drink brands like Celsius and Liquid Death water target younger demographics with edgy marketing. These brands lack legacy infrastructure costs. Digital-first approaches enable rapid iteration.
Direct-to-consumer beverage subscriptions build loyal customer bases. Personalized formulations (vitamins, adaptogens, CBD) address individual needs. Mass-market brands struggle to offer comparable customization.
Regulatory Tightening
Sugar taxes spread globally as governments combat obesity. Marketing restrictions limit advertising reach, particularly for products targeting children. Packaging regulations increase costs.
Plastic bans or bottle deposit schemes would require substantial operational changes. Front-of-package labeling highlights sugar content. Each regulatory change chips away at profitability.
Climate Change Impacts
Extreme weather disrupts supply chains and damages crops. Water scarcity limits production expansion in key markets. Coastal facilities face flooding risks as sea levels rise.
Transition risks include carbon taxes and renewable energy requirements. Physical risks manifest gradually but persistently. Adaptation costs will increase over coming decades.
PESTEL Analysis
Political Factors
Government relations critically impact operations. Coca-Cola must navigate trade policies, tax laws, and regulatory frameworks across 200+ countries.
U.S.-China tensions create complications. Tariffs on aluminum and other materials increase costs. Potential retaliatory actions by foreign governments threaten market access.
The company maintains government affairs teams in major markets. Lobbying efforts aim to shape favorable policies. However, anti-corporate sentiment limits effectiveness in some jurisdictions.
Political instability in emerging markets disrupts operations. Recent examples include Myanmar’s military coup and Venezuela’s economic collapse. The company has limited influence over geopolitical events.
Economic Factors
Macroeconomic conditions drive consumer spending patterns. Recessions reduce discretionary beverage purchases. Rising unemployment compresses demand for premium products.
Inflation affects both input costs and consumer budgets. Commodity price increases squeeze margins. Consumers trade down to private label during inflationary periods.
Currency exchange rates significantly impact reported earnings. Dollar strength hurts translation of foreign profits. Emerging market devaluations reduce local purchasing power.
Interest rates influence capital allocation decisions. Higher rates increase borrowing costs and make share buybacks relatively less attractive. Lower rates support debt-financed acquisitions.
Demographic shifts reshape beverage consumption. Aging populations in developed markets prefer different products than younger cohorts. Gen Z demands sustainability and authenticity.
Health and wellness trends accelerate. Obesity concerns drive sugar reduction. Fitness culture elevates protein drinks and sports beverages. Plant-based diets increase alternative milk consumption.
Social media amplifies consumer voices. Viral criticism damages brand reputation instantly. Conversely, positive influencer partnerships drive discovery among younger audiences.
Cultural differences require localized approaches. Flavor preferences vary dramatically across regions. Marketing messages must resonate with local values and traditions.
Technological Factors
Digitalization transforms the beverage industry. E-commerce platforms change purchase patterns. Mobile apps enable loyalty programs and personalized offers.
AI and machine learning optimize operations. Demand forecasting improves inventory management. Personalized marketing increases conversion rates. Supply chain analytics reduce waste.
Packaging technology advances. Plant-based PET bottles reduce petroleum dependence. Improved barrier properties extend shelf life. Smart packaging enables interactive consumer experiences.
Manufacturing automation increases efficiency. Robotics reduce labor costs and improve consistency. Internet-of-Things sensors enable predictive maintenance. These technologies provide cost advantages.
Environmental Factors
Climate change presents both risks and opportunities. Extreme weather threatens supply reliability. Water scarcity limits production in stressed regions. Adaptation requires significant capital investment.
Plastic pollution generates intense criticism. Ocean plastic accumulation damages marine ecosystems. Coca-Cola faces pressure to reduce packaging and increase recycling. Failure to address concerns risks consumer backlash.
Renewable energy adoption accelerates. Coca-Cola has committed to net zero emissions by 2040. Solar and wind power reduce carbon footprint. Green energy costs continue declining, improving economics.
Biodiversity concerns affect agricultural sourcing. Sustainable farming practices protect ecosystems while securing supply. Deforestation linked to sugar production invites criticism. Certification programs address concerns.
Legal Factors
Food and beverage regulations vary globally. Nutritional labeling requirements increase compliance costs. Sugar content restrictions limit formulations. Marketing rules constrain advertising approaches.
Intellectual property protection proves essential. Trademark enforcement prevents counterfeit products. Trade secret litigation protects formulations. Patent disputes arise over packaging innovations.
Labor laws affect manufacturing operations. Minimum wage increases raise production costs. Benefits requirements add overhead. Union negotiations determine wages in some markets.
Product liability concerns require careful management. Contamination incidents trigger recalls and lawsuits. Quality control systems minimize risks but cannot eliminate them entirely.
Latest Analyst Price Targets
Wall Street analysts maintain generally positive ratings on Coca-Cola. The consensus reflects confidence in the business model while acknowledging valuation concerns.
Consensus Summary:
Average Price Target: $79.08
High Target: $83.00 (BNP Paribas)
Low Target: $72.00
Current Price: ~$70.47 (as of early January 2026)
Implied Upside: 12.22%
Recent Analyst Actions:
Wall Street Zen reports analysts predict shares could reach $79.88 by November 2026.
Public.com shows 12 analysts give a consensus “Buy” rating with a 2026 average target of $78.83.
Benzinga indicates 20 analysts cover the stock with a $76.84 consensus target.
TickerNerd analysis of 27 Wall Street analysts shows a bullish consensus with $79.50 median target ranging from $72.00 to $87.00.
Rating Distribution:
Buy/Outperform: ~60% of analysts
Hold: ~35% of analysts
Sell/Underperform: ~5% of analysts
Bulls cite sustainable competitive advantages, dividend growth history, and emerging market potential. Bears worry about mature market saturation, health trends, and full valuation multiples.
Most analysts recommend holding for income-focused investors. Growth-oriented investors may find better opportunities elsewhere. However, few analysts suggest selling given the company’s fundamental strengths.
Investors should review these primary sources for detailed information:
SEC Filings:
10-K Annual Report 2024 - Comprehensive business overview and financial statements
10-Q Q3 2025 - Most recent quarterly report
Form 8-K Current Reports - Material event disclosures
Investor Relations Materials:
Q3 2025 Earnings Release - Detailed quarterly results
Investor Presentations - Management strategy discussions
Annual Reports - Shareholder communications
Earnings Call Transcripts:
Q3 2025 Transcript - Management commentary and Q&A
Prior quarter transcripts provide historical context
Corporate Website:
News Center - Press releases and updates
Sustainability Reports - ESG initiatives and progress
My Final Thoughts
The Coca-Cola Company stands at an inflection point. The business model that built a century of success faces fundamental challenges. Health-conscious consumers are abandoning sugary sodas. Younger generations view the brand as their grandparents’ beverage.
Yet dismissing Coca-Cola would be premature. The company demonstrates remarkable adaptability. Zero Sugar momentum proves consumers still want the brand, just reformulated. Acquisitions like fairlife and BODYARMOR show management recognizes the need to diversify.
For income-focused investors, Coca-Cola offers stability. The 63-year dividend growth streak provides reliability. Current yields near 3% exceed treasury bonds while offering inflation protection through dividend increases. Barring catastrophe, dividends should continue growing.
Growth investors face a tougher decision. Revenue growth of 5-6% satisfies neither aggressive return targets nor keeps pace with technology stocks. However, that comparison may be unfair. Consumer staples provide different risk-return profiles than growth stocks.
Valuation appears full but not excessive. P/E ratios around 23x reflect quality and stability. DCF analyses show sensitivity to assumptions but generally support current prices. Patient investors willing to accept mid-single-digit returns could find value.
The international footprint provides diversification. Emerging market exposure carries risks but offers upside if execution improves. China remains concerning given weak recent performance. However, India and parts of Africa show promise.
Management’s capital allocation deserves credit. Share buybacks and dividends return substantial cash to shareholders. The disciplined approach to acquisitions avoids value-destroying mega-deals. Incremental improvements compound over time.
Climate and sustainability risks require monitoring. Failure to address plastic pollution and water usage threatens long-term social license to operate. However, the company has made meaningful commitments. Execution will determine outcomes.
Competition intensifies but market leadership endures. PepsiCo remains formidable yet Coca-Cola maintains CSD dominance. Smaller brands chip away at niches but cannot replicate global scale. The moat has narrowed but not disappeared.
Investors seeking stability and income should consider Coca-Cola. Those chasing high growth should look elsewhere. As always, portfolio position sizing should reflect individual risk tolerance and objectives. No single stock should dominate a diversified portfolio.
The next twelve months will prove telling.
Can management deliver on 2026 guidance?
Does Zero Sugar momentum continue?
Will emerging markets reaccelerate?
Answers to these questions will shape the investment case through the rest of the decade.
Disclaimer: This analysis is for informational purposes only and should not be construed as investment advice. Investors should conduct their own due diligence and consult with financial advisors before making investment decisions.




Reply